Increased vaginal discharge
 Normal vaginal discharge is thin, clear or milky white and mild smelling. As your pregnancy progresses, this discharge usually becomes more noticeable, and is heaviest at the end of your pregnancy. You may want to wear an unscented panty liner. If however, the discharge becomes very smelly or the colour turns green, then you should consult your GP, as this could be a sign of a vaginal infection.
Normal vaginal discharge is thin, clear or milky white and mild smelling. As your pregnancy progresses, this discharge usually becomes more noticeable, and is heaviest at the end of your pregnancy. You may want to wear an unscented panty liner. If however, the discharge becomes very smelly or the colour turns green, then you should consult your GP, as this could be a sign of a vaginal infection.
Thrush (candida albicans) is common in pregnancy. Symptoms of thrush include; vaginal discharge that is thick, white (or tinged with pink) and can be very itchy. Consult your GP or midwife as thrush is easy to treat with a vaginal pessary and cream.
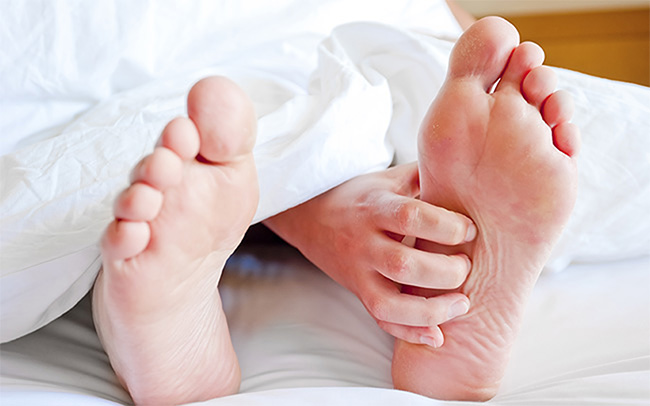 This is a liver disorder that can develop in pregnancy, usually after 30 weeks gestation, but which sometimes develop as early as 8 weeks, affecting up to one in every 140 pregnant women.
Symptoms can include:
This is a liver disorder that can develop in pregnancy, usually after 30 weeks gestation, but which sometimes develop as early as 8 weeks, affecting up to one in every 140 pregnant women.
Symptoms can include: