Immediately after giving birth
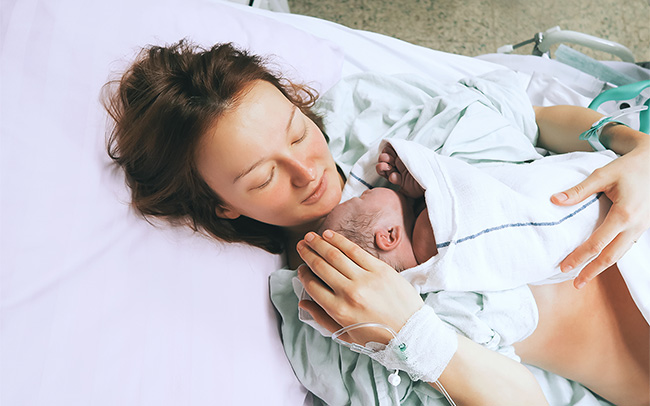


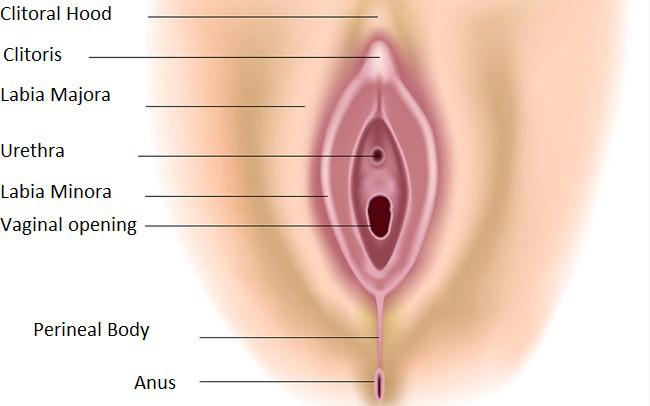 When your baby is born, his or her head stretches the opening of the vagina. The skin inside and surrounding the vagina will often stretch well to allow your baby to be born, however during this process it is common for women to sustain a tear to the inside of the vagina and/or the skin inside the vagina or both – which may require stitches. The stitches used will always be dissolvable and should not need to be removed.
First degree tears These affect the skin of the perineum/vagina. Some of these tears require stitches and some may heal well without stitches. Your midwife will advise you on this after birth.
Second degree tears These affect the skin and muscle of the perineum/vagina. Most of these tears require stitches to assist with healing.
Third and fourth degree tears These affect the skin and muscle of the perineum/vagina, as well as some of the structures associated with the anal sphincter. These tears require a repair by an obstetric doctor, under surgical conditions to repair them.
Labial tears These occur to the labia minora and will often require stitches to aid healing. Your midwife will advise you on this after birth.
Episiotomies These are sustained during the birth, when your doctor or midwife makes a cut to facilitate the birth of your baby. These are similar to second degree tears and will require stitches.
When your baby is born, his or her head stretches the opening of the vagina. The skin inside and surrounding the vagina will often stretch well to allow your baby to be born, however during this process it is common for women to sustain a tear to the inside of the vagina and/or the skin inside the vagina or both – which may require stitches. The stitches used will always be dissolvable and should not need to be removed.
First degree tears These affect the skin of the perineum/vagina. Some of these tears require stitches and some may heal well without stitches. Your midwife will advise you on this after birth.
Second degree tears These affect the skin and muscle of the perineum/vagina. Most of these tears require stitches to assist with healing.
Third and fourth degree tears These affect the skin and muscle of the perineum/vagina, as well as some of the structures associated with the anal sphincter. These tears require a repair by an obstetric doctor, under surgical conditions to repair them.
Labial tears These occur to the labia minora and will often require stitches to aid healing. Your midwife will advise you on this after birth.
Episiotomies These are sustained during the birth, when your doctor or midwife makes a cut to facilitate the birth of your baby. These are similar to second degree tears and will require stitches.
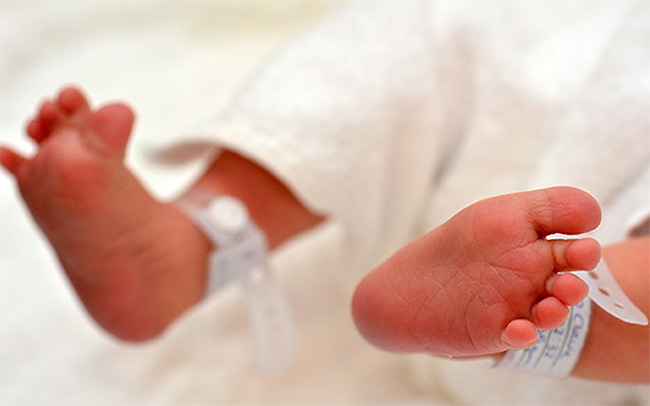 After the birth, the midwife will prepare two infant identity bands. Each band will include the mum’s surname and the hospital number. Details will be checked with the mum and/or partner against the mum’s printed patient identity band before placing it on the baby. A unique NHS number and hospital number will be generated for your baby shortly after birth. The NHS number will remain with your baby throughout their life.
After the birth, the midwife will prepare two infant identity bands. Each band will include the mum’s surname and the hospital number. Details will be checked with the mum and/or partner against the mum’s printed patient identity band before placing it on the baby. A unique NHS number and hospital number will be generated for your baby shortly after birth. The NHS number will remain with your baby throughout their life.
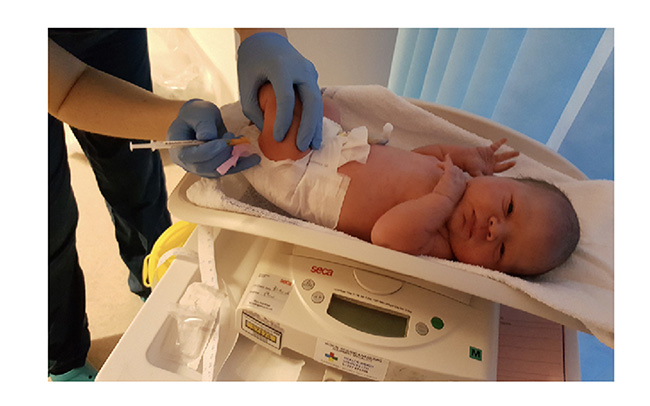 Soon after birth, your midwife will offer to give your baby vitamin K by either injection (once only) or oral drops (which are given in three doses). This is to prevent a rare but serious blood disorder, and can be given by injection or oral drops. If you opt for oral drops your baby will need to receive further doses. The decision to have oral doses may impact on future treatments until all three doses are received, for example, release of tongue tie.
Soon after birth, your midwife will offer to give your baby vitamin K by either injection (once only) or oral drops (which are given in three doses). This is to prevent a rare but serious blood disorder, and can be given by injection or oral drops. If you opt for oral drops your baby will need to receive further doses. The decision to have oral doses may impact on future treatments until all three doses are received, for example, release of tongue tie.
 During skin-to-skin contact with your baby, he or she may show early feeding cues. Your midwife will support you in feeding your baby shortly after birth. Some babies want to feed very soon after birth, whereas others take several hours to show signs that they are ready to feed.
Some babies are alert after the birth, whilst others may become sleepy. When holding your baby ensure that their nose and mouth remains unobstructed by your body, towels or clothing.
Your baby’s weight will be checked, and a midwife or neonatal doctor will check him/her from top-to-toe to exclude any major abnormalities. Your baby will be offered a supplement of Vitamin K.
In some rare cases, your baby may need to be transferred to the neonatal unit for a period of time for specialised treatment. This is more common with babies born prematurely, very small, with an infection or through a particularly complicated birth. If this happens to you, you will have plenty of support and help from your maternity team.
During skin-to-skin contact with your baby, he or she may show early feeding cues. Your midwife will support you in feeding your baby shortly after birth. Some babies want to feed very soon after birth, whereas others take several hours to show signs that they are ready to feed.
Some babies are alert after the birth, whilst others may become sleepy. When holding your baby ensure that their nose and mouth remains unobstructed by your body, towels or clothing.
Your baby’s weight will be checked, and a midwife or neonatal doctor will check him/her from top-to-toe to exclude any major abnormalities. Your baby will be offered a supplement of Vitamin K.
In some rare cases, your baby may need to be transferred to the neonatal unit for a period of time for specialised treatment. This is more common with babies born prematurely, very small, with an infection or through a particularly complicated birth. If this happens to you, you will have plenty of support and help from your maternity team.
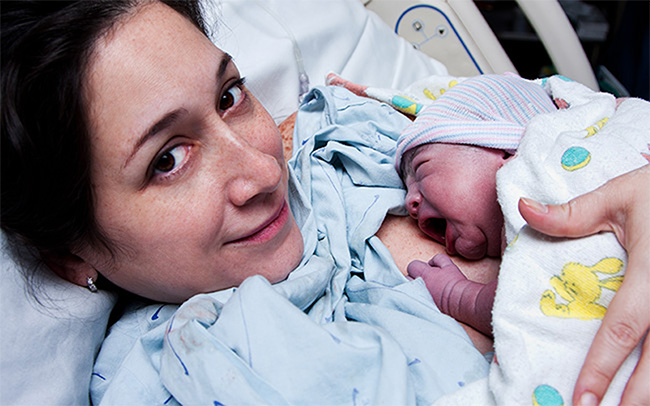 After your placenta has been delivered, your midwife or doctor will ask to check and see if you have any tears to the perineum and/or vagina that might require stitches. If you do need stitches, your midwife or doctor will explain this to you.
Before stitching your midwife or doctor will ensure the area is numbed with local anaesthetic, or if you have an epidural already, this will be topped up. Most tears will be repaired in your birthing room, more significant tears require repair in an operating theatre. Tears are repaired using dissolvable stitches and normally heal within a month of birth.
All women will lose some blood after giving birth, this happens because the area of the womb where the placenta was attached takes time to heal. Bleeding may be heavy immediately after the birth, but will reduce significantly over the next few days and weeks. Bleeding will normally last between two and six weeks. Your midwife will check on your bleeding regularly straight after birth.
If there is significant bleeding this is called a postpartum haemorrhage (PPH). Your midwife and doctor will take prompt action to stop ongoing blood loss.
After your placenta has been delivered, your midwife or doctor will ask to check and see if you have any tears to the perineum and/or vagina that might require stitches. If you do need stitches, your midwife or doctor will explain this to you.
Before stitching your midwife or doctor will ensure the area is numbed with local anaesthetic, or if you have an epidural already, this will be topped up. Most tears will be repaired in your birthing room, more significant tears require repair in an operating theatre. Tears are repaired using dissolvable stitches and normally heal within a month of birth.
All women will lose some blood after giving birth, this happens because the area of the womb where the placenta was attached takes time to heal. Bleeding may be heavy immediately after the birth, but will reduce significantly over the next few days and weeks. Bleeding will normally last between two and six weeks. Your midwife will check on your bleeding regularly straight after birth.
If there is significant bleeding this is called a postpartum haemorrhage (PPH). Your midwife and doctor will take prompt action to stop ongoing blood loss.
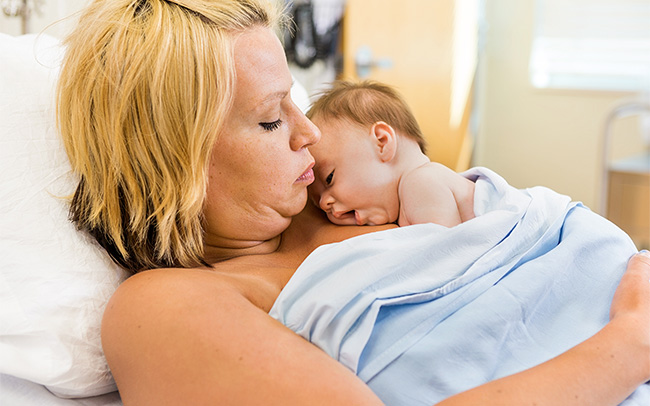 After your baby is born, so long as they are well, you will be encouraged to have immediate skin-to-skin contact. This type of contact is known to be beneficial to both mother and baby by:
After your baby is born, so long as they are well, you will be encouraged to have immediate skin-to-skin contact. This type of contact is known to be beneficial to both mother and baby by:
 Even if your baby needs help with breathing after birth, or to be seen by a neonatal doctor, you will be offered skin-to-skin contact as soon as practically possible. It is very important that your baby’s chin is free from obstruction and that a clear airway is maintained.
Read the important safety considerations in the UNICEF Baby Friendly Initiative related link below.
Even if your baby needs help with breathing after birth, or to be seen by a neonatal doctor, you will be offered skin-to-skin contact as soon as practically possible. It is very important that your baby’s chin is free from obstruction and that a clear airway is maintained.
Read the important safety considerations in the UNICEF Baby Friendly Initiative related link below.
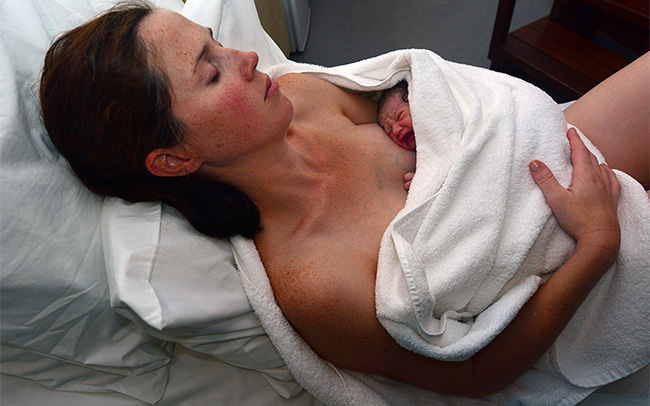 Explore what will happen once your baby has arrived.
Explore what will happen once your baby has arrived.
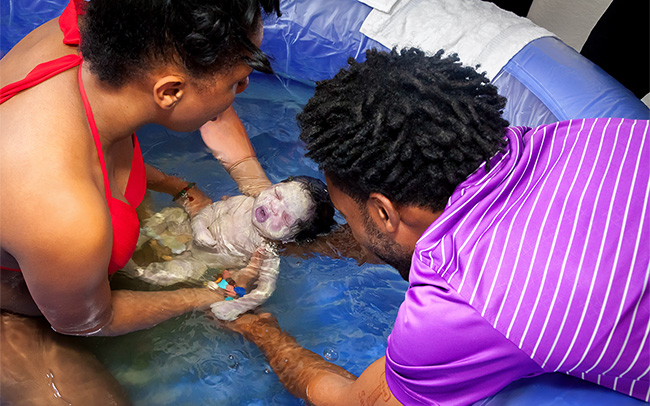 Meeting your baby for the first time can cause many different emotions in new parents. After months of build up to the birth, you may feel elation and an instant rush of love but don’t be concerned if you initially feel dazed and disconnected, or have concerns over whether the baby is alright. Making an emotional connection with your baby can take time. It is important to remember that there is no right or wrong way to feel about your newborn and that for some parents it can take quite a while to adjust to the fact that labour is over and their new baby has arrived.
Meeting your baby for the first time can cause many different emotions in new parents. After months of build up to the birth, you may feel elation and an instant rush of love but don’t be concerned if you initially feel dazed and disconnected, or have concerns over whether the baby is alright. Making an emotional connection with your baby can take time. It is important to remember that there is no right or wrong way to feel about your newborn and that for some parents it can take quite a while to adjust to the fact that labour is over and their new baby has arrived.